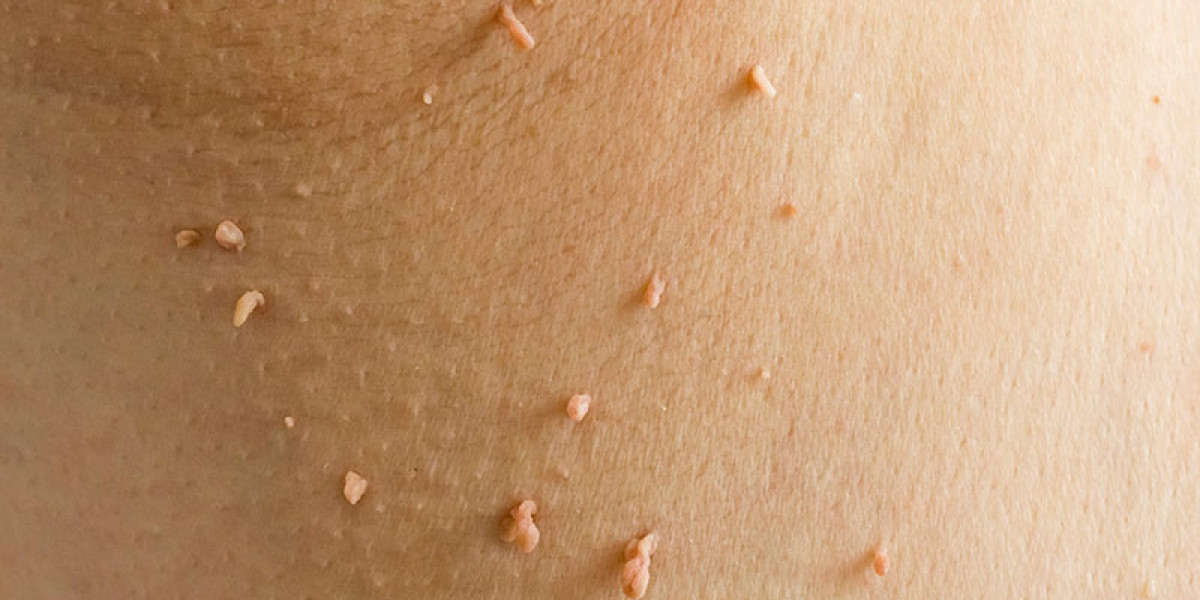
Skin tags are a common skin concern, yet many people still wonder whether they pose any risk to others. One of the most frequently asked questions is whether Skin Tags Contagious conditions exist or whether these harmless growths can spread through touch. Understanding how skin tags form, what causes them, and how they differ from infectious skin issues can help clear up confusion and reduce unnecessary worry.
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, typically appear in areas where the skin folds or experiences frequent friction. Although they are benign, their presence can cause cosmetic concerns or discomfort, especially when they catch on clothing or jewelry. Before exploring whether they are transmissible, it is essential to understand the factors behind their development and the types of people most prone to them.
In modern times, people increasingly turn to trusted digital health platforms—such as healthvore—for reliable guidance on skin conditions and wellness topics. This growing interest in online health resources highlights the need for clear, evidence-backed information to help individuals make informed decisions about their skin and overall well-being.
What Are Skin Tags?
Skin tags are small, soft growths that protrude from the skin's surface. They can vary in size from a grain of rice to a few centimeters, though most remain small and flesh-colored. These harmless growths often form on the:
Neck
Eyelids
Groin
Underarms
Under the breasts
Around skin folds
Although they may look unusual or concerning, skin tags are typically non-cancerous and painless unless irritated.
Why Skin Tags Form
Researchers believe skin tags develop due to a combination of genetic, hormonal, and physical factors. These common causes include:
Friction: Areas where skin rubs together are more prone to developing skin tags.
Genetics: Family history increases the likelihood of developing them.
Hormonal changes: Pregnant women and individuals with hormonal imbalances may experience more skin tags.
Metabolic factors: Obesity and insulin resistance are strongly associated with skin tags.
These contributing factors help explain why skin tags are common among adults of all ages, particularly those who experience increased skin friction or metabolic changes.
Are Skin Tags Contagious?
Clearing Up the Misconception
The most important fact to understand is this: skin tags are not contagious. They cannot be spread through physical contact, shared towels, hugging, or close interactions with others. Unlike viral skin conditions such as warts, skin tags do not originate from an infection.
Because they are not caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, skin tags cannot be transferred from one person to another. They develop solely based on an individual’s own skin characteristics and internal factors, not external transmission.
How Skin Tags Differ From Infectious Conditions
It is easy to confuse skin tags with other conditions that do spread from person to person, such as:
Warts caused by HPV
Molluscum contagiosum
Fungal infections
Bacterial skin infections
However, skin tags have very different features:
| Skin Tags | Viral Warts |
|---|---|
| Not contagious | Contagious |
| Caused by friction, genetics, hormones | Caused by HPV virus |
| Soft, flesh-colored | Rough, grainy |
| Often found in skin folds | Can appear anywhere |
| Painless unless irritated | Can be painful |
Understanding these differences helps reduce unnecessary fear and ensures proper treatment decisions.
Who Is Most Likely to Get Skin Tags?
Risk Factors to Consider
While anyone can develop skin tags, certain individuals are more prone to them:
Adults over 30
People with obesity
Individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance
Pregnant women
Those with a family history of skin tags
People in these categories may develop multiple skin tags over time, especially in areas where the skin folds or experiences repeated friction.
Symptoms and Appearance of Skin Tags
How to Identify Them
Skin tags are generally easy to identify due to their distinct characteristics:
Soft texture
Painless
Flesh-colored or slightly darker
A small “stalk” attaching them to the skin
No fluid or pus inside
If a growth changes color, bleeds, or becomes painful, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation, as these symptoms may indicate an underlying issue.
How to Treat or Remove Skin Tags
When Removal Is Recommended
Skin tag removal is not medically necessary unless the tag causes discomfort or cosmetic concerns. You may choose removal if the tag:
Catches on clothing or jewelry
Is located in a visible area
Causes irritation
Bleeds due to friction
Common Medical Removal Methods
Dermatologists typically use one of the following methods:
1. Cryotherapy
Freezing the skin tag with liquid nitrogen, causing it to fall off within a few days.
2. Cauterization
Using heat or electrical current to burn off the skin tag.
3. Snip Removal
Cutting the skin tag off with sterile surgical scissors or a scalpel.
4. Ligation
Tying off the tag’s blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off.
Avoid DIY Removal Risks
While home remedies exist, medical experts caution against cutting off skin tags at home due to risks such as:
Bleeding
Infection
Scarring
Improper removal
Professional removal ensures precision and reduces the risk of complications.
Can Skin Tags Be Prevented?
Prevention Tips
Since skin tags are influenced by genetics and bodily changes, complete prevention is not guaranteed. However, you can lower your risk by:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Reducing friction in skin folds
Keeping skin dry in moisture-prone areas
Managing blood sugar levels
Wearing breathable clothing
These lifestyle adjustments can reduce the likelihood of developing new skin tags over time.
When to See a Dermatologist
Although skin tags are harmless, it is wise to consult a dermatologist if:
The growth rapidly changes in size or color
It bleeds without apparent cause
It becomes painful
You are unsure whether the growth is a skin tag
Healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose the growth and recommend the safest removal method.
Final Thoughts
Skin tags are extremely common and completely harmless, despite the confusion surrounding their nature. The most crucial takeaway is that they are not contagious and pose no threat to others. They are simply benign growths caused by friction, genetics, and metabolic factors—not an infection or virus.
If you have skin tags and are worried about their appearance or comfort, modern dermatological treatments offer safe and effective removal options. Understanding the realities behind skin tags empowers you to manage them with confidence and clarity, free from unnecessary worry or misinformation.