The rise of blockchain technology has brought unprecedented opportunities for decentralization, transparency, and security. However, one of the key challenges facing blockchain networks today is maintaining user privacy while ensuring data integrity. Enter zero knowledge proof crypto an innovative cryptographic method that allows one party to prove knowledge of certain information without revealing the information itself. This technology is transforming the way blockchains handle sensitive data, offering both security and privacy for users across multiple applications.
In this article, we’ll explore what zero knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are, how they work, their benefits and challenges, tokenomics where applicable, practical use cases, and why they are poised to become a foundational technology in the crypto space.
Understanding Zero Knowledge Proofs
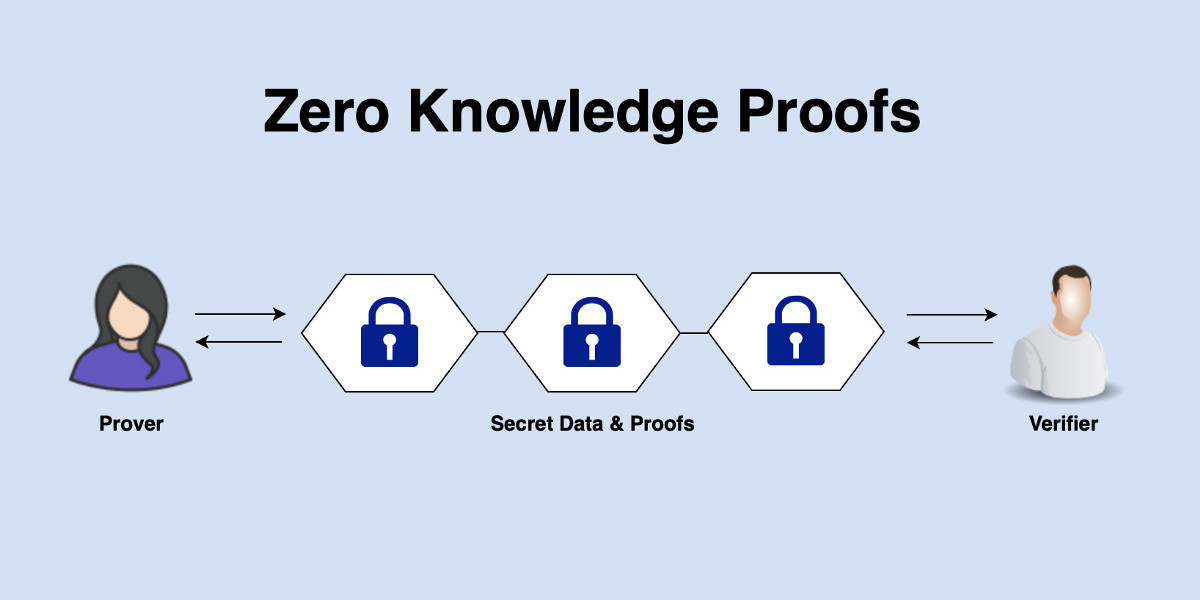
At its core, a zero knowledge proof is a cryptographic protocol in which one party, called the prover, can convince another party, called the verifier, that a statement is true without revealing any other information beyond the validity of that statement. Imagine proving that you know the password to a system without ever disclosing the password itself. This ability is crucial for privacy-focused applications, where sensitive information must remain confidential yet verifiable.
In the context of crypto, ZKPs are most commonly used in blockchain transactions. For example, they can verify that a transaction is legitimate without exposing sender or receiver identities, transaction amounts, or other sensitive details. This capability not only enhances privacy but also reduces the risk of data breaches and malicious activity.
How Zero Knowledge Proof Crypto Works
Zero knowledge proof systems typically rely on complex mathematical algorithms and cryptography. There are two primary types of ZKPs used in blockchain networks:
Interactive ZKPs: Require multiple rounds of interaction between the prover and the verifier. These systems involve back-and-forth communication to confirm the validity of a claim.
Non-interactive ZKPs (NIZK): Allow a proof to be generated and verified independently, without repeated communication, making them more scalable and suitable for blockchain applications.
Protocols such as zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) and zk-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge) are leading the way in implementing ZKPs in crypto. These protocols vary in terms of computational requirements, scalability, and transparency, but all aim to provide secure verification without compromising privacy.
Key Features and Benefits
Zero knowledge proof crypto offers several features that make it highly attractive for blockchain developers and users:
Enhanced Privacy: Transactions can be verified without revealing sensitive information.
Data Security: Sensitive user data stays private, reducing exposure to hackers or leaks.
Scalability: Some ZKP protocols reduce the amount of data required for verification, enabling faster and more efficient networks.
Regulatory Compliance: ZKPs can allow selective disclosure, helping platforms comply with regulations without sacrificing privacy.
These features make zero knowledge proofs particularly useful for financial applications, identity verification, confidential smart contracts, and decentralized exchanges.
Tokenomics in Zero Knowledge Proof Projects
Several crypto projects incorporate zero knowledge proofs into their blockchain ecosystems, each with unique tokenomics that drive network growth and incentivize participants. Typically, tokens in ZKP-based projects serve multiple purposes:
Utility Tokens: Used to pay transaction fees or access privacy-focused features.
Governance Tokens: Allow holders to vote on protocol upgrades, scaling solutions, or changes to privacy rules.
Incentive Mechanisms: Reward participants for contributing to network security, proof generation, or staking.
For example, a hypothetical ZKP crypto token might have a total supply of 1 billion tokens, with 40% allocated to community incentives, 30% to the development team, 20% for private investors, and 10% reserved for ecosystem partnerships. Clear and transparent tokenomics ensure that investors understand how value is distributed and how their participation impacts the network.
Practical Use Cases
Zero knowledge proofs are not just theoretical; they are actively applied in various blockchain projects:
Privacy Coins: Cryptocurrencies like Zcash use zk-SNARKs to enable fully private transactions.
DeFi Platforms: ZKPs can verify financial transactions without revealing the details, enhancing security and trust.
Identity Verification: Users can prove credentials without exposing personal data, useful for KYC processes and secure logins.
Supply Chain Management: Verifying the authenticity of goods without revealing sensitive business information.
These applications demonstrate how zero knowledge proof crypto is solving real-world problems while maintaining blockchain integrity and decentralization.
Challenges and Considerations
While zero knowledge proofs offer significant advantages, they also face challenges:
Computational Complexity: Generating and verifying proofs can be resource-intensive, requiring optimization for large-scale networks.
Adoption Barriers: Integrating ZKPs into existing systems requires technical expertise and careful protocol design.
Regulatory Ambiguity: Privacy-focused features may raise concerns with regulators, necessitating a balance between anonymity and compliance.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development are continuously improving ZKP protocols, making them more efficient, scalable, and practical for mainstream adoption.
Roadmap and Future Potential
The roadmap for zero knowledge proof crypto projects often includes milestones such as:
Protocol Upgrades: Implementing faster and more scalable ZKPs like zk-STARKs.
Ecosystem Expansion: Partnering with DeFi platforms, identity services, and enterprise blockchain solutions.
Mainstream Adoption: Enabling broader use cases in finance, healthcare, and supply chain sectors.
As blockchain technology evolves, zero knowledge proofs are expected to become an essential building block for secure, privacy-preserving networks.
Conclusion
Zero knowledge proof crypto represents a significant leap forward in blockchain privacy, security, and efficiency. By allowing transactions and claims to be verified without revealing sensitive information, ZKPs protect users while maintaining network integrity. With transparent tokenomics, practical applications in finance and identity, and a clear roadmap for innovation, these projects are well-positioned to shape the future of decentralized technology.
For investors and developers looking for blockchain solutions that balance transparency with privacy, zero knowledge proof crypto offers a compelling opportunity to engage with next-generation technology that solves real-world problems while pushing the boundaries of digital security.